React原理
深入了解 React 原理,如何用 400 行代码 构建你自己的 React.js
React v19 beta 已经发布。与 React 18 相比,它提供了许多用户友好的 API,尽管其核心原理基本保持不变。你可能已经使用 React 一段时间了,但你了解它的内部工作原理吗?
本文将帮助你构建一个大约 400 行代码的 React 版本,它支持异步更新并且可以被中断——这是 React 的一个核心特性,许多更高级的 API 都依赖于它。这是最终效果的 GIF:
我使用了 React 官方网站提供的井字棋教程示例,可以看到它运行得很好。
它目前托管在我的 GitHub 上,你也可以访问在线版本亲自尝试。

GitHub - ZacharyL2/mini-react: 用 400 行代码实现 Mini-React,一个具有异步可中断更新的最小模型。
用 400 行代码实现 Mini-React,一个具有异步可中断更新的最小模型。 - ZacharyL2/mini-react
github.com/ZacharyL2/mini-react「JSX 和 createElement」
在深入探讨 mini-react.ts 的原理之前,理解 JSX 代表什么非常重要。我们可以使用 JSX 来描述 DOM,并轻松应用 JavaScript 逻辑。然而,浏览器并不原生理解 JSX,所以我们编写的 JSX 被编译成浏览器能理解的 JavaScript。
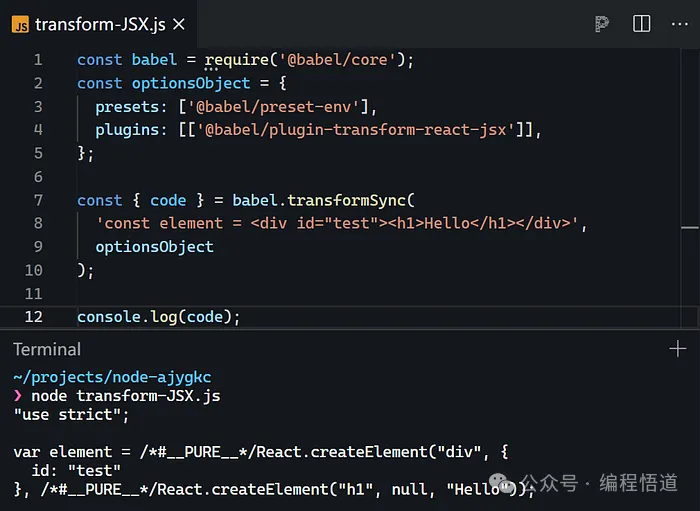
你可以看到它调用了 React.createElement,它提供了以下选项:
type:表示当前节点的类型,如 div。
props:表示当前元素节点的属性,例如 {id: "test"}。
children:子元素,可以是多个元素、简单文本或由 React.createElemen 创建的更多节点。
如果你是经验丰富的 React 用户,你可能会记得,在 React 18 之前,你需要导入 React 才能正确编写 JSX。自 React 18 以来,这不再必要,这增强了开发者体验,但在底层 React.createElement 仍然被调用。
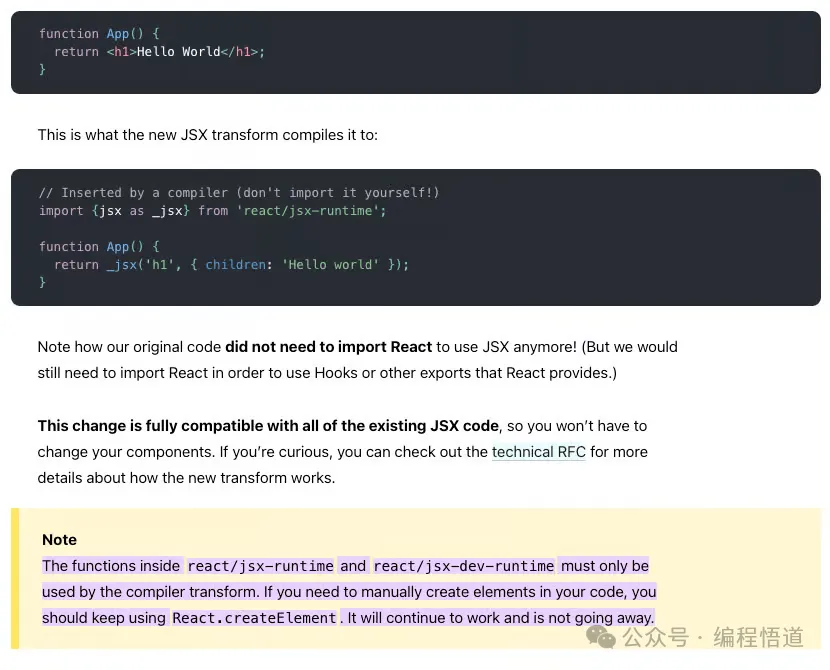

对于我们的简化 React 实现,我们需要在配置 Vite 时设置 react({ jsxRuntime: 'classic' })。
然后我们可以实现我们自己的:
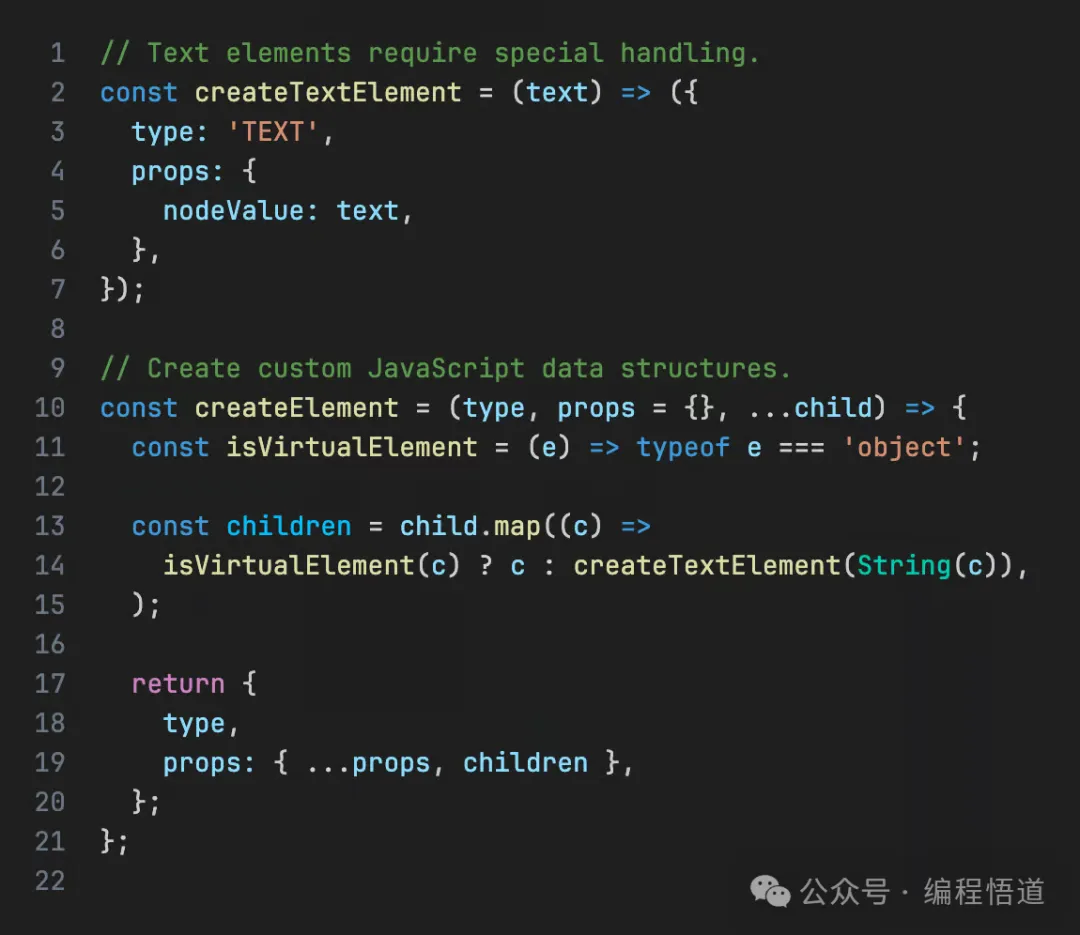
「渲染」
接下来,我们基于之前创建的数据结构实现一个简化版的渲染函数,将 JSX 渲染到真实的 DOM。
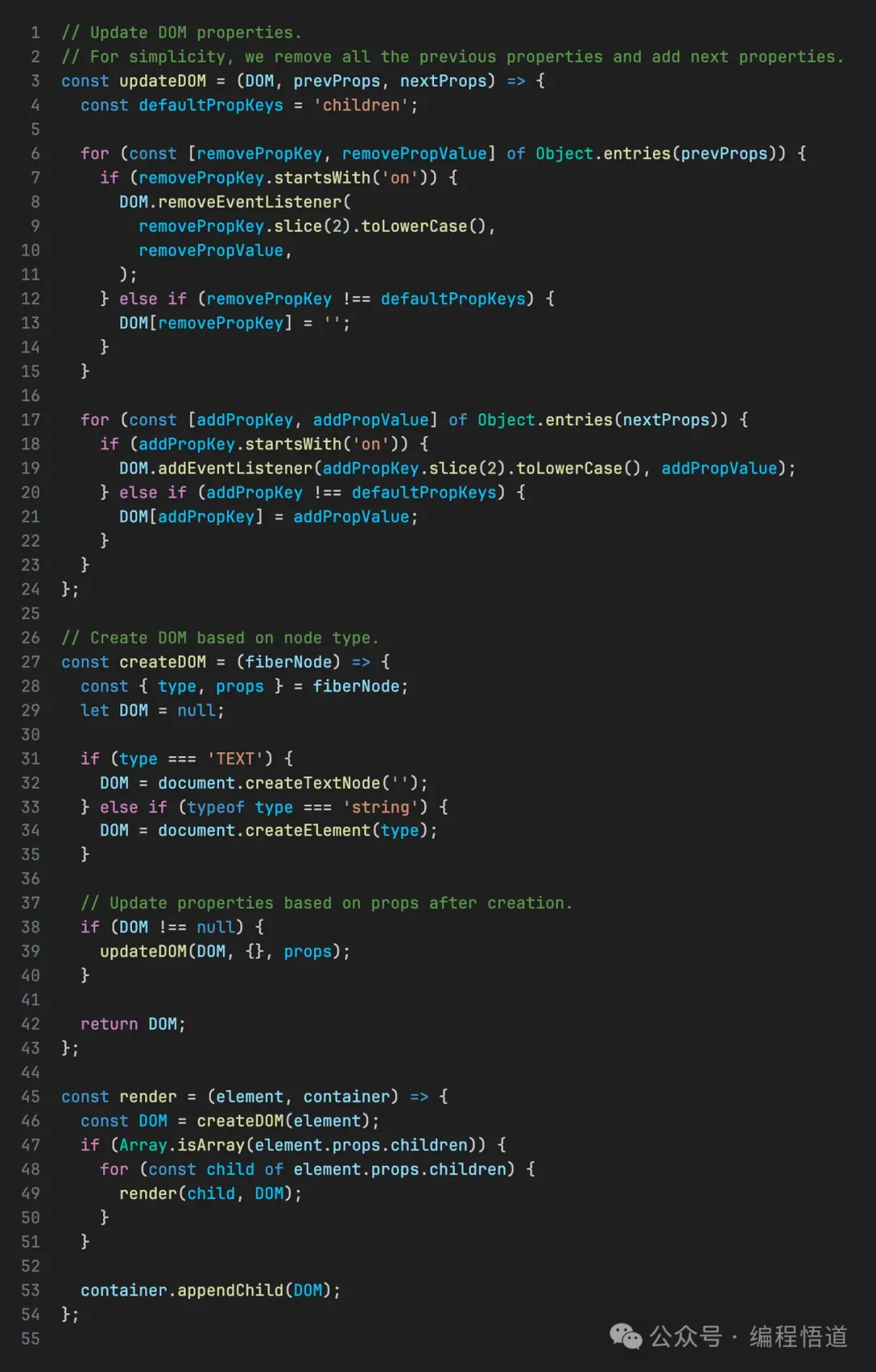
这是在线实现链接。它目前只渲染一次 JSX,因此不处理交互。
「Fiber 架构和并发模式」
Fiber 架构和并发模式主要是为了解决一旦递归遍历完整个元素树,它就不能被中断,可能会长时间阻塞主线程的问题。高优先级任务,如用户输入或动画,可能无法及时处理。
在 React 的源代码中,工作被分解成小单元。每当浏览器空闲时,它处理这些小工作单元,将主线程的控制权交还给浏览器,以便浏览器能够及时响应高优先级任务。一旦一个工作的所有必要小单元都完成,结果就会被映射到真实的 DOM。
两个关键点是如何放弃主线程的控制权,以及如何将工作分解成可管理的单元。
「requestIdleCallback」
requestIdleCallback 是一个实验性 API,它在浏览器空闲时执行回调。它尚未被所有浏览器支持。在 React 中,它在调度程序包中使用,该包具有比 requestIdleCallback 更复杂的调度逻辑,包括更新任务优先级。
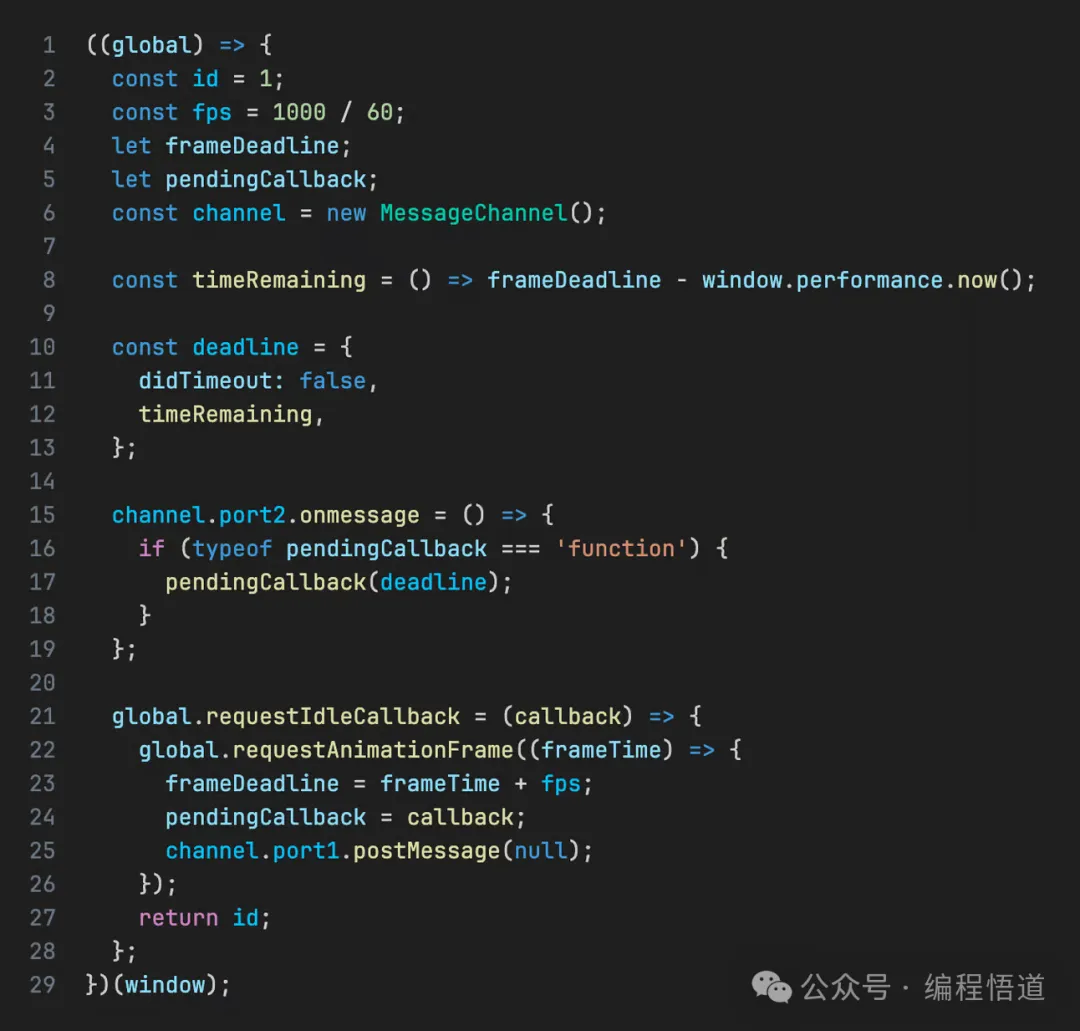
但我们在这里只考虑异步可中断性,所以这是模仿 React 的基本实现:
「以下是一些关键点的简要说明:」
为什么使用 MessageChannel?
主要是,它使用宏任务来处理每一轮的单元任务。但为什么是宏任务?
这是因为我们需要使用宏任务来放弃主线程的控制权,允许浏览器在这个空闲期间更新 DOM 或接收事件。由于浏览器将 DOM 更新作为一个单独的任务,此时不执行 JavaScript。
主线程一次只能运行一个任务——要么执行 JavaScript,要么处理 DOM 计算、样式计算、输入事件等。然而,微任务并不放弃主线程的控制权。
为什么不用 setTimeout?
这是因为现代浏览器认为超过五次的嵌套 setTimeout 调用是阻塞的,并将它们的最小延迟设置为 4 毫秒,所以它不够精确。
「算法」
请注意,React 不断发展,我描述的算法可能不是最新的,但它们足以理解其基本原理。
这是显示工作单元之间联系的图表:
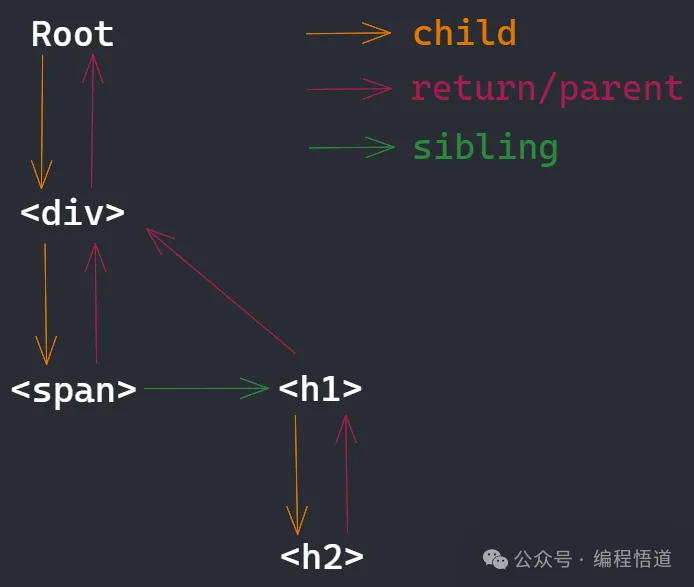
在 React 中,每个工作单元被称为一个 Fiber 节点。它们使用类似链表的结构相互链接:
child:从父节点指向第一个子元素的指针。
return/parent:所有子元素都有一个指针回到父元素。
sibling:从第一个子元素指向下一个兄弟元素。
有了这个数据结构,让我们看看具体的实现。
我们只是扩展了渲染逻辑,重新构建了调用序列,以 workLoop -> performUnitOfWork -> reconcileChildren -> commitRoot 的顺序工作。
workLoop:通过连续调用 requestIdleCallback 来获取空闲时间。如果当前处于空闲状态并且有单元任务要执行,那么执行每个单元任务。
performUnitOfWork:执行的具体单元任务。这是链表思想的体现。具体来说,一次只处理一个 fiber 节点,并返回下一个要处理的节点。
reconcileChildren:协调当前 fiber 节点,实际上是虚拟 DOM 的比较,并记录要进行的更改。你可以看到我们直接修改并保存在每个 fiber 节点上,因为现在它只是 JavaScript 对象的修改,并没有触及真实的 DOM。
commitRoot:如果当前需要更新(根据 wipRoot)并且没有下一个单元任务要处理(根据 !nextUnitOfWork),这意味着虚拟更改需要映射到真实的 DOM。commitRoot 是根据 fiber 节点的变化修改真实的 DOM。
有了这些,我们才能真正使用 fiber 架构进行可中断的 DOM 更新,但我们仍然缺少一个触发器。
「触发更新」
在 React 中,最常见的触发器是 useState,这是最基本的更新机制。让我们实现它来点燃我们的 Fiber 引擎。
这是具体的实现,简化成一个函数:
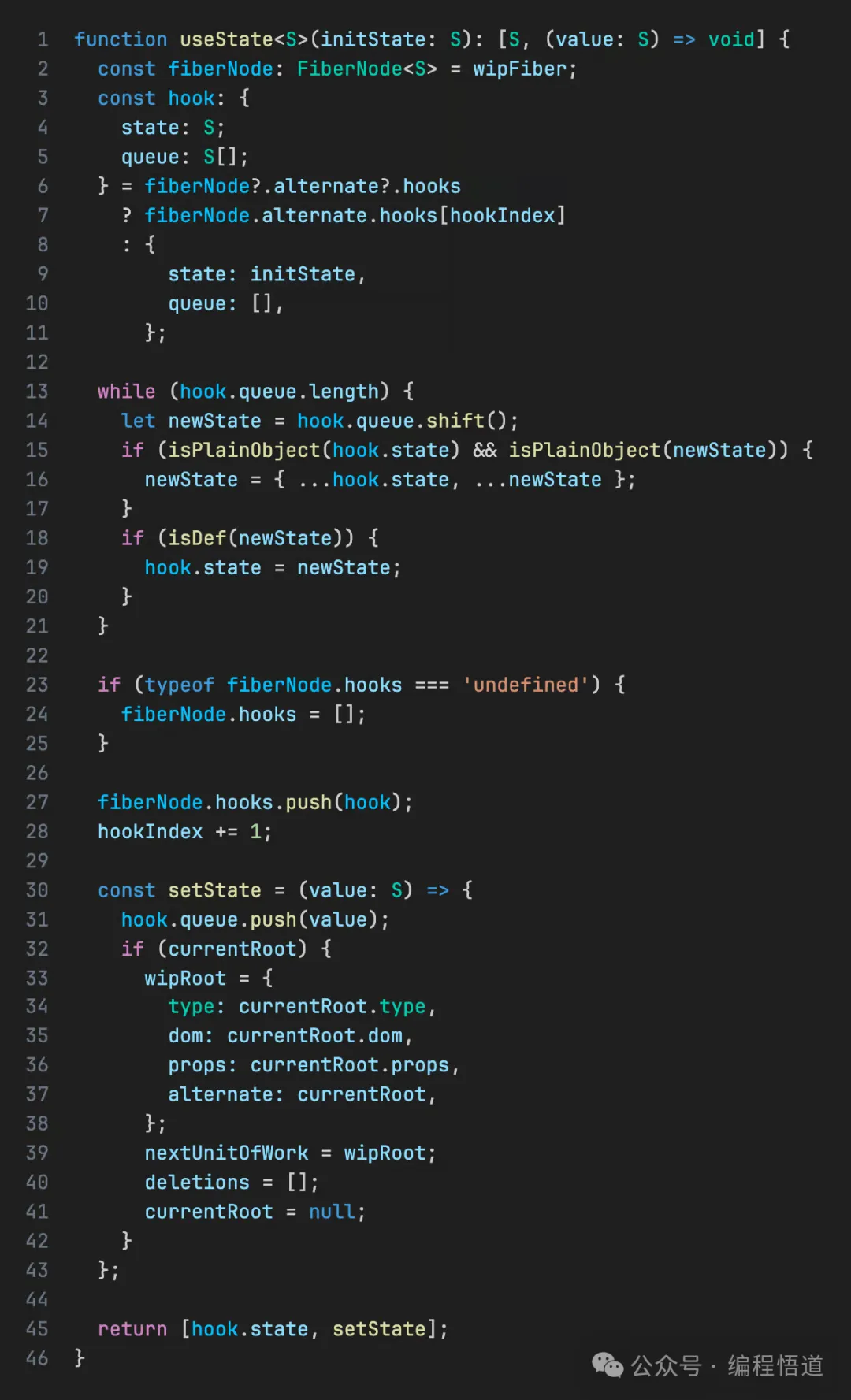
它巧妙地将钩子的状态保持在 fiber 节点上,并通过队列修改状态。从这里,你还可以看到为什么 React 钩子调用的顺序不能改变。
源码部分
- src/App.jsx
// Forked from https://reactjs.org/tutorial/tutorial.html#what-are-we-building
import React from './mini-react';
const { useState } = React;
function Square({ value, onSquareClick }) {
return (
<button className="square" onClick={onSquareClick}>
{value}
</button>
);
}
function Board({ xIsNext, squares, onPlay }) {
function handleClick(i) {
if (calculateWinner(squares) || squares[i]) {
return;
}
const nextSquares = squares.slice();
if (xIsNext) {
nextSquares[i] = 'X';
} else {
nextSquares[i] = 'O';
}
onPlay(nextSquares);
}
const winner = calculateWinner(squares);
let status;
if (winner) {
status = 'Winner: ' + winner;
} else {
status = 'Next player: ' + (xIsNext ? 'X' : 'O');
}
return (
<>
<div className="status">{status}</div>
<div className="board-row">
<Square value={squares[0]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(0)} />
<Square value={squares[1]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(1)} />
<Square value={squares[2]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(2)} />
</div>
<div className="board-row">
<Square value={squares[3]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(3)} />
<Square value={squares[4]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(4)} />
<Square value={squares[5]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(5)} />
</div>
<div className="board-row">
<Square value={squares[6]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(6)} />
<Square value={squares[7]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(7)} />
<Square value={squares[8]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(8)} />
</div>
</>
);
}
export default function Game() {
const [history, setHistory] = useState([Array(9).fill(null)]);
const [currentMove, setCurrentMove] = useState(0);
const xIsNext = currentMove % 2 === 0;
const currentSquares = history[currentMove];
function handlePlay(nextSquares) {
const nextHistory = [...history.slice(0, currentMove + 1), nextSquares];
setHistory(nextHistory);
setCurrentMove(nextHistory.length - 1);
}
function jumpTo(nextMove) {
setCurrentMove(nextMove);
}
const moves = history.map((squares, move) => {
let description;
if (move > 0) {
description = 'Go to move #' + move;
} else {
description = 'Go to game start';
}
return (
<li key={move}>
<button onClick={() => jumpTo(move)}>{description}</button>
</li>
);
});
return (
<div className="game">
<div className="game-board">
<Board xIsNext={xIsNext} squares={currentSquares} onPlay={handlePlay} />
</div>
<div className="game-info">
<ol>{moves}</ol>
</div>
</div>
);
}
function calculateWinner(squares) {
const lines = [
[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 3, 6],
[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[0, 4, 8],
[2, 4, 6],
];
for (let i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) {
const [a, b, c] = lines[i];
if (squares[a] && squares[a] === squares[b] && squares[a] === squares[c]) {
return squares[a];
}
}
return null;
}- src/LegacyClassApp.jsx
import React from './mini-react';
function calculateWinner(squares) {
const lines = [
[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 3, 6],
[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[0, 4, 8],
[2, 4, 6],
];
for (let i = 0; i < lines.length; i += 1) {
const [a, b, c] = lines[i];
if (squares[a] && squares[a] === squares[b] && squares[a] === squares[c]) {
return squares[a];
}
}
return null;
}
class Square extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.props.onClick} className="square">
{this.props.value}
</button>
);
}
}
class Board extends React.Component {
renderSquare(i) {
return (
<Square
value={this.props.squares[i]}
onClick={() => {
this.props.onClick(i);
}}
/>
);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<div className="board-row">
{this.renderSquare(0)}
{this.renderSquare(1)}
{this.renderSquare(2)}
</div>
<div className="board-row">
{this.renderSquare(3)}
{this.renderSquare(4)}
{this.renderSquare(5)}
</div>
<div className="board-row">
{this.renderSquare(6)}
{this.renderSquare(7)}
{this.renderSquare(8)}
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
history: [
{
squares: Array(9).fill(null),
},
],
stepNumber: 0,
xIsNext: true,
};
}
handleClick(i) {
const history = this.state.history.slice(0, this.state.stepNumber + 1);
const current = history[history.length - 1];
const squares = current.squares.slice();
if (calculateWinner(squares) || squares[i]) {
return;
}
squares[i] = this.state.xIsNext ? 'X' : 'O';
this.setState({
history: history.concat([
{
squares,
},
]),
stepNumber: history.length,
xIsNext: !this.state.xIsNext,
});
}
jumpTo(step) {
this.setState({
stepNumber: step,
xIsNext: step % 2 === 0,
});
}
render() {
const { history } = this.state;
const current = history[this.state.stepNumber];
const winner = calculateWinner(current.squares);
const moves = history.map((step, move) => {
const desc = move ? `Go to move #${move}` : 'Go to game start';
return (
<li key={move}>
<button onClick={() => this.jumpTo(move)}>{desc}</button>
</li>
);
});
let status;
if (winner) {
status = `Winner: ${winner}`;
} else {
status = `Next player: ${this.state.xIsNext ? 'X' : 'O'}`;
}
return (
<div className="game">
<div className="game-board">
<Board
squares={current.squares}
onClick={(i) => {
this.handleClick(i);
}}
/>
</div>
<div className="game-info">
<div>{status}</div>
<ol>{moves}</ol>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;- src/index.jsx
// Forked from https://reactjs.org/tutorial/tutorial.html#what-are-we-building
import React from './mini-react';
import App from './App'; // OR `LegacyClassApp`
import './styles.css';
React.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));- src/mini-react.ts
// TODO Optimization Type Description
interface ComponentFunction {
new (props: Record<string, unknown>): Component;
(props: Record<string, unknown>): VirtualElement | string;
}
type VirtualElementType = ComponentFunction | string;
interface VirtualElementProps {
children?: VirtualElement[];
[propName: string]: unknown;
}
interface VirtualElement {
type: VirtualElementType;
props: VirtualElementProps;
}
type FiberNodeDOM = Element | Text | null | undefined;
interface FiberNode<S = any> extends VirtualElement {
alternate: FiberNode<S> | null;
dom?: FiberNodeDOM;
effectTag?: string;
child?: FiberNode;
return?: FiberNode;
sibling?: FiberNode;
hooks?: {
state: S;
queue: S[];
}[];
}
let wipRoot: FiberNode | null = null;
let nextUnitOfWork: FiberNode | null = null;
let currentRoot: FiberNode | null = null;
let deletions: FiberNode[] = [];
let wipFiber: FiberNode;
let hookIndex = 0;
// Support React.Fragment syntax.
const Fragment = Symbol.for('react.fragment');
// Enhanced requestIdleCallback.
((global: Window) => {
const id = 1;
const fps = 1e3 / 60;
let frameDeadline: number;
let pendingCallback: IdleRequestCallback;
const channel = new MessageChannel();
const timeRemaining = () => frameDeadline - window.performance.now();
const deadline = {
didTimeout: false,
timeRemaining,
};
channel.port2.onmessage = () => {
if (typeof pendingCallback === 'function') {
pendingCallback(deadline);
}
};
global.requestIdleCallback = (callback: IdleRequestCallback) => {
global.requestAnimationFrame((frameTime) => {
frameDeadline = frameTime + fps;
pendingCallback = callback;
channel.port1.postMessage(null);
});
return id;
};
})(window);
const isDef = <T>(param: T): param is NonNullable<T> =>
param !== void 0 && param !== null;
const isPlainObject = (val: unknown): val is Record<string, unknown> =>
Object.prototype.toString.call(val) === '[object Object]' &&
[Object.prototype, null].includes(Object.getPrototypeOf(val));
// Simple judgment of virtual elements.
const isVirtualElement = (e: unknown): e is VirtualElement =>
typeof e === 'object';
// Text elements require special handling.
const createTextElement = (text: string): VirtualElement => ({
type: 'TEXT',
props: {
nodeValue: text,
},
});
// Create custom JavaScript data structures.
const createElement = (
type: VirtualElementType,
props: Record<string, unknown> = {},
...child: (unknown | VirtualElement)[]
): VirtualElement => {
const children = child.map((c) =>
isVirtualElement(c) ? c : createTextElement(String(c)),
);
return {
type,
props: {
...props,
children,
},
};
};
// Update DOM properties.
// For simplicity, we remove all the previous properties and add next properties.
const updateDOM = (
DOM: NonNullable<FiberNodeDOM>,
prevProps: VirtualElementProps,
nextProps: VirtualElementProps,
) => {
const defaultPropKeys = 'children';
for (const [removePropKey, removePropValue] of Object.entries(prevProps)) {
if (removePropKey.startsWith('on')) {
DOM.removeEventListener(
removePropKey.slice(2).toLowerCase(),
removePropValue as EventListener,
);
} else if (removePropKey !== defaultPropKeys) {
// @ts-expect-error: Unreachable code error
DOM[removePropKey] = '';
}
}
for (const [addPropKey, addPropValue] of Object.entries(nextProps)) {
if (addPropKey.startsWith('on')) {
DOM.addEventListener(
addPropKey.slice(2).toLowerCase(),
addPropValue as EventListener,
);
} else if (addPropKey !== defaultPropKeys) {
// @ts-expect-error: Unreachable code error
DOM[addPropKey] = addPropValue;
}
}
};
// Create DOM based on node type.
const createDOM = (fiberNode: FiberNode): FiberNodeDOM => {
const { type, props } = fiberNode;
let DOM: FiberNodeDOM = null;
if (type === 'TEXT') {
DOM = document.createTextNode('');
} else if (typeof type === 'string') {
DOM = document.createElement(type);
}
// Update properties based on props after creation.
if (DOM !== null) {
updateDOM(DOM, {}, props);
}
return DOM;
};
// Change the DOM based on fiber node changes.
// Note that we must complete the comparison of all fiber nodes before commitRoot.
// The comparison of fiber nodes can be interrupted, but the commitRoot cannot be interrupted.
const commitRoot = () => {
const findParentFiber = (fiberNode?: FiberNode) => {
if (fiberNode) {
let parentFiber = fiberNode.return;
while (parentFiber && !parentFiber.dom) {
parentFiber = parentFiber.return;
}
return parentFiber;
}
return null;
};
const commitDeletion = (
parentDOM: FiberNodeDOM,
DOM: NonNullable<FiberNodeDOM>,
) => {
if (isDef(parentDOM)) {
parentDOM.removeChild(DOM);
}
};
const commitReplacement = (
parentDOM: FiberNodeDOM,
DOM: NonNullable<FiberNodeDOM>,
) => {
if (isDef(parentDOM)) {
parentDOM.appendChild(DOM);
}
};
const commitWork = (fiberNode?: FiberNode) => {
if (fiberNode) {
if (fiberNode.dom) {
const parentFiber = findParentFiber(fiberNode);
const parentDOM = parentFiber?.dom;
switch (fiberNode.effectTag) {
case 'REPLACEMENT':
commitReplacement(parentDOM, fiberNode.dom);
break;
case 'UPDATE':
updateDOM(
fiberNode.dom,
fiberNode.alternate ? fiberNode.alternate.props : {},
fiberNode.props,
);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
commitWork(fiberNode.child);
commitWork(fiberNode.sibling);
}
};
for (const deletion of deletions) {
if (deletion.dom) {
const parentFiber = findParentFiber(deletion);
commitDeletion(parentFiber?.dom, deletion.dom);
}
}
if (wipRoot !== null) {
commitWork(wipRoot.child);
currentRoot = wipRoot;
}
wipRoot = null;
};
// Reconcile the fiber nodes before and after, compare and record the differences.
const reconcileChildren = (
fiberNode: FiberNode,
elements: VirtualElement[] = [],
) => {
let index = 0;
let oldFiberNode: FiberNode | undefined = void 0;
let prevSibling: FiberNode | undefined = void 0;
const virtualElements = elements.flat(Infinity);
if (fiberNode.alternate?.child) {
oldFiberNode = fiberNode.alternate.child;
}
while (
index < virtualElements.length ||
typeof oldFiberNode !== 'undefined'
) {
const virtualElement = virtualElements[index];
let newFiber: FiberNode | undefined = void 0;
const isSameType = Boolean(
oldFiberNode &&
virtualElement &&
oldFiberNode.type === virtualElement.type,
);
if (isSameType && oldFiberNode) {
newFiber = {
type: oldFiberNode.type,
dom: oldFiberNode.dom,
alternate: oldFiberNode,
props: virtualElement.props,
return: fiberNode,
effectTag: 'UPDATE',
};
}
if (!isSameType && Boolean(virtualElement)) {
newFiber = {
type: virtualElement.type,
dom: null,
alternate: null,
props: virtualElement.props,
return: fiberNode,
effectTag: 'REPLACEMENT',
};
}
if (!isSameType && oldFiberNode) {
deletions.push(oldFiberNode);
}
if (oldFiberNode) {
oldFiberNode = oldFiberNode.sibling;
}
if (index === 0) {
fiberNode.child = newFiber;
} else if (typeof prevSibling !== 'undefined') {
prevSibling.sibling = newFiber;
}
prevSibling = newFiber;
index += 1;
}
};
// Execute each unit task and return to the next unit task.
// Different processing according to the type of fiber node.
const performUnitOfWork = (fiberNode: FiberNode): FiberNode | null => {
const { type } = fiberNode;
switch (typeof type) {
case 'function': {
wipFiber = fiberNode;
wipFiber.hooks = [];
hookIndex = 0;
let children: ReturnType<ComponentFunction>;
if (Object.getPrototypeOf(type).REACT_COMPONENT) {
const C = type;
const component = new C(fiberNode.props);
const [state, setState] = useState(component.state);
component.props = fiberNode.props;
component.state = state;
component.setState = setState;
children = component.render.bind(component)();
} else {
children = type(fiberNode.props);
}
reconcileChildren(fiberNode, [
isVirtualElement(children)
? children
: createTextElement(String(children)),
]);
break;
}
case 'number':
case 'string':
if (!fiberNode.dom) {
fiberNode.dom = createDOM(fiberNode);
}
reconcileChildren(fiberNode, fiberNode.props.children);
break;
case 'symbol':
if (type === Fragment) {
reconcileChildren(fiberNode, fiberNode.props.children);
}
break;
default:
if (typeof fiberNode.props !== 'undefined') {
reconcileChildren(fiberNode, fiberNode.props.children);
}
break;
}
if (fiberNode.child) {
return fiberNode.child;
}
let nextFiberNode: FiberNode | undefined = fiberNode;
while (typeof nextFiberNode !== 'undefined') {
if (nextFiberNode.sibling) {
return nextFiberNode.sibling;
}
nextFiberNode = nextFiberNode.return;
}
return null;
};
// Use requestIdleCallback to query whether there is currently a unit task
// and determine whether the DOM needs to be updated.
const workLoop: IdleRequestCallback = (deadline) => {
while (nextUnitOfWork && deadline.timeRemaining() > 1) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
if (!nextUnitOfWork && wipRoot) {
commitRoot();
}
window.requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
};
// Initial or reset.
const render = (element: VirtualElement, container: Element) => {
currentRoot = null;
wipRoot = {
type: 'div',
dom: container,
props: {
children: [{ ...element }],
},
alternate: currentRoot,
};
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot;
deletions = [];
};
abstract class Component {
props: Record<string, unknown>;
abstract state: unknown;
abstract setState: (value: unknown) => void;
abstract render: () => VirtualElement;
constructor(props: Record<string, unknown>) {
this.props = props;
}
// Identify Component.
static REACT_COMPONENT = true;
}
// Associate the hook with the fiber node.
function useState<S>(initState: S): [S, (value: S) => void] {
const fiberNode: FiberNode<S> = wipFiber;
const hook: {
state: S;
queue: S[];
} = fiberNode?.alternate?.hooks
? fiberNode.alternate.hooks[hookIndex]
: {
state: initState,
queue: [],
};
while (hook.queue.length) {
let newState = hook.queue.shift();
if (isPlainObject(hook.state) && isPlainObject(newState)) {
newState = { ...hook.state, ...newState };
}
if (isDef(newState)) {
hook.state = newState;
}
}
if (typeof fiberNode.hooks === 'undefined') {
fiberNode.hooks = [];
}
fiberNode.hooks.push(hook);
hookIndex += 1;
const setState = (value: S) => {
hook.queue.push(value);
if (currentRoot) {
wipRoot = {
type: currentRoot.type,
dom: currentRoot.dom,
props: currentRoot.props,
alternate: currentRoot,
};
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot;
deletions = [];
currentRoot = null;
}
};
return [hook.state, setState];
}
// Start the engine!
void (function main() {
window.requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
})();
export default {
createElement,
render,
useState,
Component,
Fragment,
};「结论」
我们已经实现了一个支持异步和可中断更新的最小 React 模型,没有依赖项,并且不包括注释和类型,它可能少于 400 行代码。我希望这对你有所帮助。
