1. Composition API(常用部分)
1) setup
- 新的 option, 所有的组合 API 函数都在此使用, 只在初始化时执行一次
- 函数如果返回对象, 对象中的属性或方法, 模板中可以直接使用
2) ref
- 作用: 定义一个数据的响应式
- 语法: const xxx = ref(initValue):
- 创建一个包含响应式数据的引用(reference)对象
- js 中操作数据: xxx.value
- 模板中操作数据: 不需要.value
- 一般用来定义一个基本类型的响应式数据
vue
<template>
<h2>{{ count }}</h2>
<hr />
<button @click="update">更新</button>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from "vue";
export default {
/* 在Vue3中依然可以使用data和methods配置, 但建议使用其新语法实现 */
// data () {
// return {
// count: 0
// }
// },
// methods: {
// update () {
// this.count++
// }
// }
/* 使用vue3的composition API */
setup() {
// 定义响应式数据 ref对象
const count = ref(1);
console.log(count);
// 更新响应式数据的函数
function update() {
// alert('update')
count.value = count.value + 1;
}
return {
count,
update,
};
},
};
</script>3) reactive
- 作用: 定义多个数据的响应式
- const proxy = reactive(obj): 接收一个普通对象然后返回该普通对象的响应式代理器对象
- 响应式转换是“深层的”:会影响对象内部所有嵌套的属性
- 内部基于 ES6 的 Proxy 实现,通过代理对象操作源对象内部数据都是响应式的
vue
<template>
<h2>name: {{ state.name }}</h2>
<h2>age: {{ state.age }}</h2>
<h2>wife: {{ state.wife }}</h2>
<hr />
<button @click="update">更新</button>
</template>
<script>
/*
reactive:
作用: 定义多个数据的响应式
const proxy = reactive(obj): 接收一个普通对象然后返回该普通对象的响应式代理器对象
响应式转换是“深层的”:会影响对象内部所有嵌套的属性
内部基于 ES6 的 Proxy 实现,通过代理对象操作源对象内部数据都是响应式的
*/
import { reactive } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
/*
定义响应式数据对象
*/
const state = reactive({
name: "tom",
age: 25,
wife: {
name: "marry",
age: 22,
},
});
console.log(state, state.wife);
const update = () => {
state.name += "--";
state.age += 1;
state.wife.name += "++";
state.wife.age += 2;
};
return {
state,
update,
};
},
};
</script>4) 比较 Vue2 与 Vue3 的响应式(重要)
vue2 的响应式
- 核心:
- 对象: 通过 defineProperty 对对象的已有属性值的读取和修改进行劫持(监视/拦截)
- 数组: 通过重写数组更新数组一系列更新元素的方法来实现元素修改的劫持
javascript
Object.defineProperty(data, "count", {
get() {},
set() {},
});- 问题
- 对象直接新添加的属性或删除已有属性, 界面不会自动更新
- 直接通过下标替换元素或更新 length, 界面不会自动更新 arr[1] = {}
Vue3 的响应式
- 核心:
- 通过 Proxy(代理): 拦截对 data 任意属性的任意(13 种)操作, 包括属性值的读写, 属性的添加, 属性的删除等...
- 通过 Reflect(反射): 动态对被代理对象的相应属性进行特定的操作
- 文档:
js
new Proxy(data, {
// 拦截读取属性值
get(target, prop) {
return Reflect.get(target, prop);
},
// 拦截设置属性值或添加新属性
set(target, prop, value) {
return Reflect.set(target, prop, value);
},
// 拦截删除属性
deleteProperty(target, prop) {
return Reflect.deleteProperty(target, prop);
},
});
proxy.name = "tom";html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Proxy 与 Reflect</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const user = {
name: "John",
age: 12,
};
/*
proxyUser是代理对象, user是被代理对象
后面所有的操作都是通过代理对象来操作被代理对象内部属性
*/
const proxyUser = new Proxy(user, {
get(target, prop) {
console.log("劫持get()", prop);
return Reflect.get(target, prop);
},
set(target, prop, val) {
console.log("劫持set()", prop, val);
return Reflect.set(target, prop, val); // (2)
},
deleteProperty(target, prop) {
console.log("劫持delete属性", prop);
return Reflect.deleteProperty(target, prop);
},
});
// 读取属性值
console.log(proxyUser === user);
console.log(proxyUser.name, proxyUser.age);
// 设置属性值
proxyUser.name = "bob";
proxyUser.age = 13;
console.log(user);
// 添加属性
proxyUser.sex = "男";
console.log(user);
// 删除属性
delete proxyUser.sex;
console.log(user);
</script>
</body>
</html>5) setup 细节
setup 执行的时机
- 在 beforeCreate 之前执行(一次), 此时组件对象还没有创建
- this 是 undefined, 不能通过 this 来访问 data/computed/methods / props
- 其实所有的 composition API 相关回调函数中也都不可以
setup 的返回值
- 一般都返回一个对象: 为模板提供数据, 也就是模板中可以直接使用此对象中的所有属性/方法
- 返回对象中的属性会与 data 函数返回对象的属性合并成为组件对象的属性
- 返回对象中的方法会与 methods 中的方法合并成功组件对象的方法
- 如果有重名, setup 优先
- 注意:
- 一般不要混合使用: methods 中可以访问 setup 提供的属性和方法, 但在 setup 方法中不能访问 data 和 methods
- setup 不能是一个 async 函数: 因为返回值不再是 return 的对象, 而是 promise, 模板看不到 return 对象中的属性数据
setup 的参数
- setup(props, context) / setup(props, {attrs, slots, emit})
- props: 包含 props 配置声明且传入了的所有属性的对象
- attrs: 包含没有在 props 配置中声明的属性的对象, 相当于 this.$attrs
- slots: 包含所有传入的插槽内容的对象, 相当于 this.$slots
- emit: 用来分发自定义事件的函数, 相当于 this.$emit
vue
<template>
<h2>App</h2>
<p>msg: {{ msg }}</p>
<button @click="fn('--')">更新</button>
<child :msg="msg" msg2="cba" @fn="fn" />
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { reactive, ref } from "vue";
import child from "./child.vue";
export default {
components: {
child,
},
setup() {
const msg = ref("abc");
function fn(content: string) {
msg.value += content;
}
return {
msg,
fn,
};
},
};
</script>vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>{{ n }}</h3>
<h3>{{ m }}</h3>
<h3>msg: {{ msg }}</h3>
<h3>msg2: {{ $attrs.msg2 }}</h3>
<slot name="xxx"></slot>
<button @click="update">更新</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { ref, defineComponent } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "child",
props: ["msg"],
emits: ["fn"], // 可选的, 声明了更利于程序员阅读, 且可以对分发的事件数据进行校验
data() {
console.log("data", this);
return {
// n: 1
};
},
beforeCreate() {
console.log("beforeCreate", this);
},
methods: {
// update () {
// this.n++
// this.m++
// }
},
// setup (props, context) {
setup(props, { attrs, emit, slots }) {
console.log("setup", this);
console.log(props.msg, attrs.msg2, slots, emit);
const m = ref(2);
const n = ref(3);
function update() {
// console.log('--', this)
// this.n += 2
// this.m += 2
m.value += 2;
n.value += 2;
// 分发自定义事件
emit("fn", "++");
}
return {
m,
n,
update,
};
},
});
</script>6) reactive 与 ref-细节
- 是 Vue3 的 composition API 中 2 个最重要的响应式 API
- ref 用来处理基本类型数据, reactive 用来处理对象(递归深度响应式)
- 如果用 ref 对象/数组, 内部会自动将对象/数组转换为 reactive 的代理对象
- ref 内部: 通过给 value 属性添加 getter/setter 来实现对数据的劫持
- reactive 内部: 通过使用 Proxy 来实现对对象内部所有数据的劫持, 并通过 Reflect 操作对象内部数据
- ref 的数据操作: 在 js 中要.value, 在模板中不需要(内部解析模板时会自动添加.value)
vue
<template>
<h2>App</h2>
<p>m1: {{ m1 }}</p>
<p>m2: {{ m2 }}</p>
<p>m3: {{ m3 }}</p>
<button @click="update">更新</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { reactive, ref } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const m1 = ref("abc");
const m2 = reactive({ x: 1, y: { z: "abc" } });
// 使用ref处理对象 ==> 对象会被自动reactive为proxy对象
const m3 = ref({ a1: 2, a2: { a3: "abc" } });
console.log(m1, m2, m3);
console.log(m3.value.a2); // 也是一个proxy对象
function update() {
m1.value += "--";
m2.x += 1;
m2.y.z += "++";
m3.value = { a1: 3, a2: { a3: "abc---" } };
m3.value.a2.a3 += "=="; // reactive对对象进行了深度数据劫持
console.log(m3.value.a2);
}
return {
m1,
m2,
m3,
update,
};
},
};
</script>7) 计算属性与监视
computed 函数:
- 与 computed 配置功能一致
- 只有 getter
- 有 getter 和 setter
watch 函数
- 与 watch 配置功能一致
- 监视指定的一个或多个响应式数据, 一旦数据变化, 就自动执行监视回调
- 默认初始时不执行回调, 但可以通过配置 immediate 为 true, 来指定初始时立即执行第一次
- 通过配置 deep 为 true, 来指定深度监视
watchEffect 函数
- 不用直接指定要监视的数据, 回调函数中使用的哪些响应式数据就监视哪些响应式数据
- 默认初始时就会执行第一次, 从而可以收集需要监视的数据
- 监视数据发生变化时回调
vue
<template>
<h2>App</h2>
fistName:
<input v-model="user.firstName" />
<br />
lastName:
<input v-model="user.lastName" />
<br />
fullName1:
<input v-model="fullName1" />
<br />
fullName2:
<input v-model="fullName2" />
<br />
fullName3:
<input v-model="fullName3" />
<br />
</template>
<script lang="ts">
/*
计算属性与监视
1. computed函数:
与computed配置功能一致
只有getter
有getter和setter
2. watch函数
与watch配置功能一致
监视指定的一个或多个响应式数据, 一旦数据变化, 就自动执行监视回调
默认初始时不执行回调, 但可以通过配置immediate为true, 来指定初始时立即执行第一次
通过配置deep为true, 来指定深度监视
3. watchEffect函数
不用直接指定要监视的数据, 回调函数中使用的哪些响应式数据就监视哪些响应式数据
默认初始时就会执行第一次, 从而可以收集需要监视的数据
监视数据发生变化时回调
*/
import { reactive, ref, computed, watch, watchEffect } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const user = reactive({
firstName: "A",
lastName: "B",
});
// 只有getter的计算属性
const fullName1 = computed(() => {
console.log("fullName1");
return user.firstName + "-" + user.lastName;
});
// 有getter与setter的计算属性
const fullName2 = computed({
get() {
console.log("fullName2 get");
return user.firstName + "-" + user.lastName;
},
set(value: string) {
console.log("fullName2 set");
const names = value.split("-");
user.firstName = names[0];
user.lastName = names[1];
},
});
const fullName3 = ref("");
/*
watchEffect: 监视所有回调中使用的数据
*/
/*
watchEffect(() => {
console.log('watchEffect')
fullName3.value = user.firstName + '-' + user.lastName
})
*/
/*
使用watch的2个特性:
深度监视
初始化立即执行
*/
watch(
user,
() => {
fullName3.value = user.firstName + "-" + user.lastName;
},
{
immediate: true, // 是否初始化立即执行一次, 默认是false
deep: true, // 是否是深度监视, 默认是false
}
);
/*
watch一个数据
默认在数据发生改变时执行回调
*/
watch(fullName3, (value) => {
console.log("watch");
const names = value.split("-");
user.firstName = names[0];
user.lastName = names[1];
});
/*
watch监听多个数据:
使用数组来指定
如果是ref对象, 直接指定
如果是reactive对象中的属性, 必须通过函数来指定
user里面的属性非响应式数据,需要使用回调方式 () = > 属性 ,改成响应式属性
*/
watch([() => user.firstName, () => user.lastName, fullName3], (values) => {
console.log("监视多个数据", values);
});
return {
user,
fullName1,
fullName2,
fullName3,
};
},
};
</script>8) 生命周期
vue2.x 的生命周期:
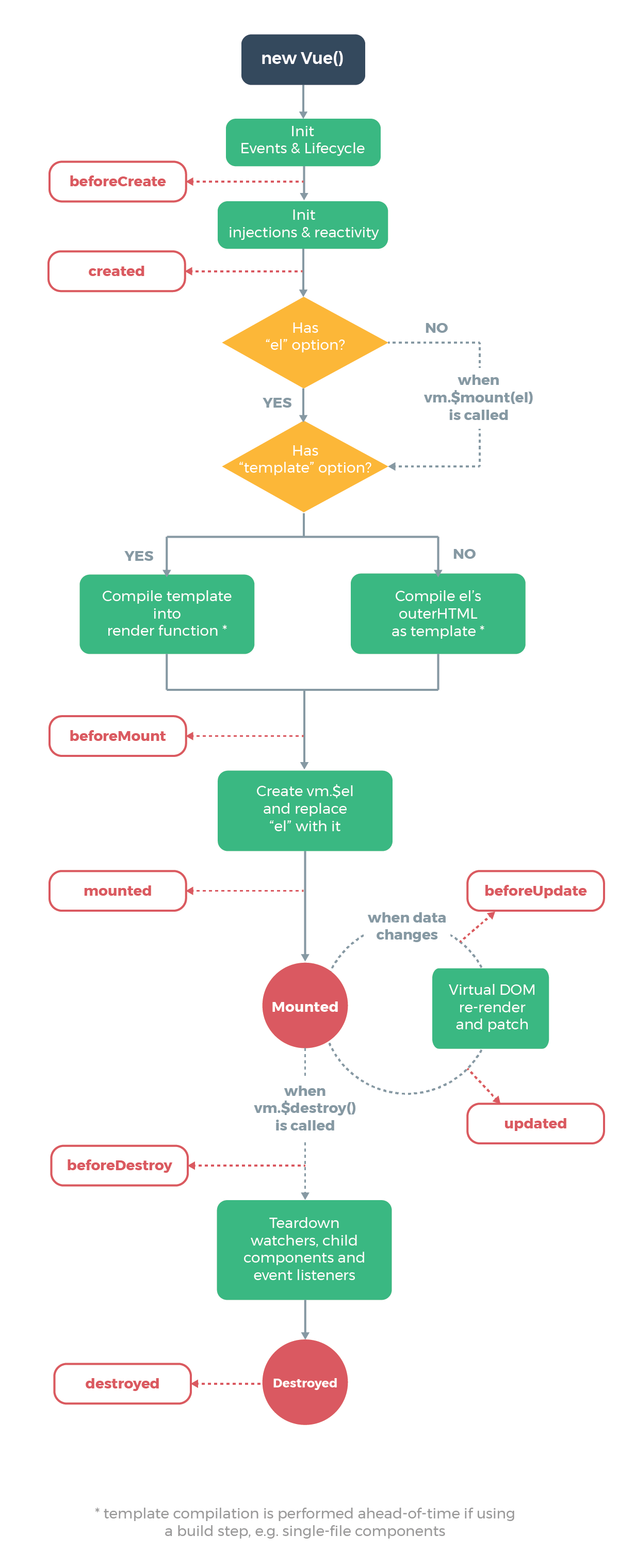
vue3 的生命周期:
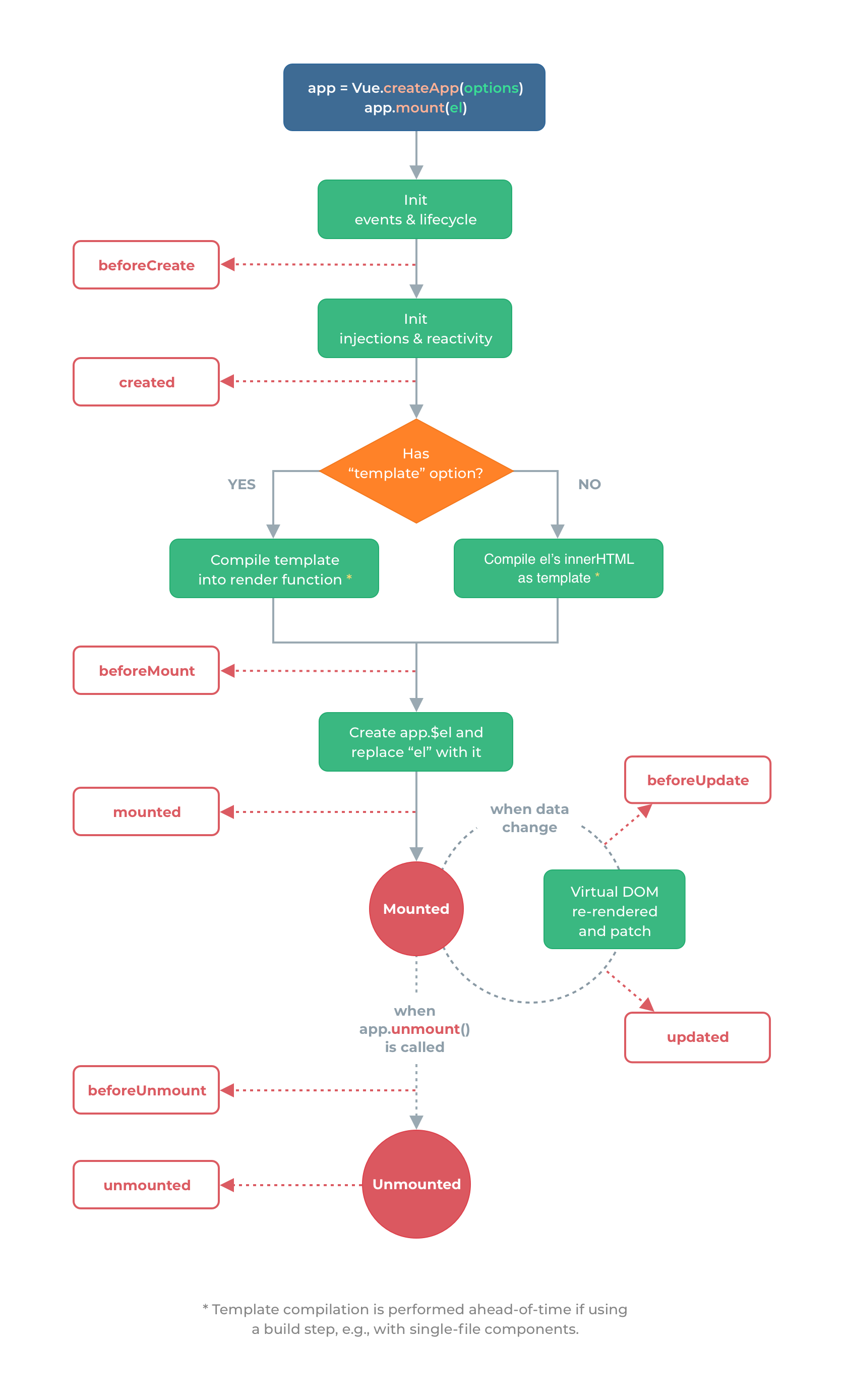
与 2.x 版本生命周期相对应的组合式 API:
beforeCreate-> 使用setup()created-> 使用setup()beforeMount->onBeforeMountmounted->onMountedbeforeUpdate->onBeforeUpdateupdated->onUpdatedbeforeDestroy->onBeforeUnmountdestroyed->onUnmountederrorCaptured->onErrorCaptured
新增的钩子函数:
组合式 API 还提供了以下调试钩子函数:
- onRenderTracked
- onRenderTriggered
vue
<template>
<div class="about">
<h2>msg: {{ msg }}</h2>
<hr />
<button @click="update">更新</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
ref,
onMounted,
onUpdated,
onUnmounted,
onBeforeMount,
onBeforeUpdate,
onBeforeUnmount,
} from "vue";
export default {
beforeCreate() {
console.log("beforeCreate()");
},
created() {
console.log("created");
},
beforeMount() {
console.log("beforeMount");
},
mounted() {
console.log("mounted");
},
beforeUpdate() {
console.log("beforeUpdate");
},
updated() {
console.log("updated");
},
beforeUnmount() {
console.log("beforeUnmount");
},
unmounted() {
console.log("unmounted");
},
setup() {
const msg = ref("abc");
const update = () => {
msg.value += "--";
};
onBeforeMount(() => {
console.log("--onBeforeMount");
});
onMounted(() => {
console.log("--onMounted");
});
onBeforeUpdate(() => {
console.log("--onBeforeUpdate");
});
onUpdated(() => {
console.log("--onUpdated");
});
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
console.log("--onBeforeUnmount");
});
onUnmounted(() => {
console.log("--onUnmounted");
});
return {
msg,
update,
};
},
};
</script>vue
<template>
<h2>App</h2>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">切换</button>
<hr />
<Child v-if="isShow" />
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import Child from "./Child.vue";
export default {
data() {
return {
isShow: true,
};
},
components: {
Child,
},
};
</script>09) 自定义 hook 函数
使用 Vue3 的组合 API 封装的可复用的功能函数
自定义 hook 的作用类似于 vue2 中的 mixin 技术
自定义 Hook 的优势: 很清楚复用功能代码的来源, 更清楚易懂
需求 1: 收集用户鼠标点击的页面坐标
hooks/useMousePosition.ts
js
import { ref, onMounted, onUnmounted } from "vue";
/*
收集用户鼠标点击的页面坐标
*/
export default function useMousePosition() {
// 初始化坐标数据
const x = ref(-1);
const y = ref(-1);
// 用于收集点击事件坐标的函数
const updatePosition = (e: MouseEvent) => {
x.value = e.pageX;
y.value = e.pageY;
};
// 挂载后绑定点击监听
onMounted(() => {
document.addEventListener("click", updatePosition);
});
// 卸载前解绑点击监听
onUnmounted(() => {
document.removeEventListener("click", updatePosition);
});
return { x, y };
}vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>x: {{ x }}, y: {{ y }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from "vue";
/*
在组件中引入并使用自定义hook
自定义hook的作用类似于vue2中的mixin技术
自定义Hook的优势: 很清楚复用功能代码的来源, 更清楚易懂
*/
import useMousePosition from "./hooks/useMousePosition";
export default {
setup() {
const { x, y } = useMousePosition();
return {
x,
y,
};
},
};
</script>利用 TS 泛型强化类型检查
需求 2: 封装发 ajax 请求的 hook 函数
hooks/useRequest.ts
ts
import { ref } from "vue";
import axios from "axios";
/*
使用axios发送异步ajax请求
*/
export default function useUrlLoader<T>(url: string) {
const result = ref<T | null>(null);
const loading = ref(true);
const errorMsg = ref(null);
axios
.get(url)
.then((response) => {
loading.value = false;
result.value = response.data;
})
.catch((e) => {
loading.value = false;
errorMsg.value = e.message || "未知错误";
});
return {
loading,
result,
errorMsg,
};
}vue
<template>
<div class="about">
<h2 v-if="loading">LOADING...</h2>
<h2 v-else-if="errorMsg">{{ errorMsg }}</h2>
<!-- <ul v-else>
<li>id: {{result.id}}</li>
<li>name: {{result.name}}</li>
<li>distance: {{result.distance}}</li>
</ul> -->
<ul v-for="p in result" :key="p.id">
<li>id: {{ p.id }}</li>
<li>title: {{ p.title }}</li>
<li>price: {{ p.price }}</li>
</ul>
<!-- <img v-if="result" :src="result[0].url" alt=""> -->
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { watch } from "vue";
import useRequest from "./hooks/useRequest";
// 地址数据接口
interface AddressResult {
id: number;
name: string;
distance: string;
}
// 产品数据接口
interface ProductResult {
id: string;
title: string;
price: number;
}
export default {
setup() {
// const {loading, result, errorMsg} = useRequest<AddressResult>('/data/address.json')
const { loading, result, errorMsg } = useRequest<ProductResult[]>(
"/data/products.json"
);
watch(result, () => {
if (result.value) {
console.log(result.value.length); // 有提示
}
});
return {
loading,
result,
errorMsg,
};
},
};
</script>10) toRefs
把一个响应式对象转换成普通对象,该普通对象的每个 property 都是一个 ref
应用: 当从合成函数返回响应式对象时,toRefs 非常有用,这样消费组件就可以在不丢失响应式的情况下对返回的对象进行分解使用
问题: reactive 对象取出的所有属性值都是非响应式的
解决: 利用 toRefs 可以将一个响应式 reactive 对象的所有原始属性转换为响应式的 ref 属性
vue
<template>
<h2>App</h2>
<h3>foo: {{ foo }}</h3>
<h3>bar: {{ bar }}</h3>
<h3>foo2: {{ foo2 }}</h3>
<h3>bar2: {{ bar2 }}</h3>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { reactive, toRefs } from "vue";
/*
toRefs:
将响应式对象中所有属性包装为ref对象, 并返回包含这些ref对象的普通对象
应用: 当从合成函数返回响应式对象时,toRefs 非常有用,
这样消费组件就可以在不丢失响应式的情况下对返回的对象进行分解使用
*/
export default {
setup() {
const state = reactive({
foo: "a",
bar: "b",
});
const stateAsRefs = toRefs(state);
setTimeout(() => {
state.foo += "++";
state.bar += "++";
}, 2000);
const { foo2, bar2 } = useReatureX();
return {
// ...state,
...stateAsRefs,
foo2,
bar2,
};
},
};
function useReatureX() {
const state = reactive({
foo2: "a",
bar2: "b",
});
setTimeout(() => {
state.foo2 += "++";
state.bar2 += "++";
}, 2000);
return toRefs(state);
}
</script>11) ref 获取元素
利用 ref 函数获取组件中的标签元素
功能需求: 让输入框自动获取焦点
vue
<template>
<h2>App</h2>
<input type="text" />
---
<input type="text" ref="inputRef" />
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { onMounted, ref } from "vue";
/*
ref获取元素: 利用ref函数获取组件中的标签元素
功能需求: 让输入框自动获取焦点
*/
export default {
setup() {
const inputRef = ref<HTMLElement | null>(null);
onMounted(() => {
inputRef.value && inputRef.value.focus();
});
return {
inputRef,
};
},
};
</script>